Radon is a silent threat that can seep into well water, exposing families to hidden dangers. Unlike other contaminants, radon is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, making it nearly impossible to detect without proper testing.
If you rely on well water, understanding the risks of radon exposure is crucial. This guide explains what radon is, how it gets into well water, the health risks it poses, and—most importantly—how to remove it effectively.
What is Radon and Why Should You Be Concerned?
Radon is a radioactive gas that forms when uranium breaks down in soil and rock. Since it’s naturally occurring, radon can find its way into homes through air and water, often without homeowners realizing it.Understanding Radon’s Origins
Radon is produced from the decay of uranium found in soil, rock, and groundwater. As a gas, it easily moves through the ground and can enter homes through foundation cracks, plumbing, and well water. Most people associate radon with airborne exposure, but waterborne radon is just as concerning. When radon-contaminated water is used for drinking, cooking, or showering, the gas can be released into indoor air, leading to inhalation exposure.How Radon Gets Into Well Water
Radon dissolves into groundwater as it moves through uranium-rich rock formations. This makes private wells, especially deep wells, more susceptible to contamination. Unlike municipal water systems that treat and aerate water before distribution, private well owners bear the responsibility of testing and treating their own water supply. Radon can enter a well through:- Direct contact with uranium-containing bedrock.
- Cracks or fissures in underground aquifers.
- Poorly sealed well casings that allow soil gases to enter.
The Hidden Health Risks of Radon in Well Water
Many homeowners are unaware of the risks associated with radon in their drinking water. This invisible hazard can lead to severe health issues over time.Inhalation vs. Ingestion – Which is More Dangerous?
Radon exposure happens in two main ways:- Inhalation: When radon gas is released from water during daily activities like showering, washing dishes, or doing laundry. Prolonged inhalation can lead to lung cancer, as radon decays into radioactive particles that get trapped in lung tissue.
- Ingestion: When radon-contaminated water is consumed directly, it can damage the internal organs. Long-term ingestion has been linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer and gastrointestinal issues, as radon decays into harmful radioactive elements inside the digestive system.
Common Symptoms of Radon Exposure
Radon exposure doesn’t cause immediate symptoms, making it difficult to detect. Long-term exposure has been linked to:- Increased risk of lung cancer – Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking.
- Respiratory issues – Prolonged exposure can lead to shortness of breath and lung inflammation.
- Persistent coughing – A chronic cough that doesn’t improve with typical treatments.
- Chest pain – Discomfort that can worsen over time.
- Increased risk of stomach cancer – Due to radon-contaminated water being ingested and absorbed through the digestive tract.
- Fatigue and headaches – Prolonged exposure may result in unexplained tiredness and cognitive issues.
How to Test for Radon in Well Water
Testing is the only way to determine if radon is present in your well water. Fortunately, testing is straightforward and affordable.Recommended Testing Methods
- Home Radon Test Kits – These provide an initial reading and are simple to use, but they may not be as accurate as professional testing.
- Professional Radon Testing – Certified specialists use advanced methods to obtain precise measurements and ensure accurate results.
Understanding Your Test Results
Radon levels in water are measured in picocuries per liter (pCi/L). The EPA recommends action if radon levels exceed 4,000 pCi/L in water or 4.0 pCi/L in air. If levels are high, immediate mitigation measures should be taken.The Best Ways to Remove Radon from Well Water
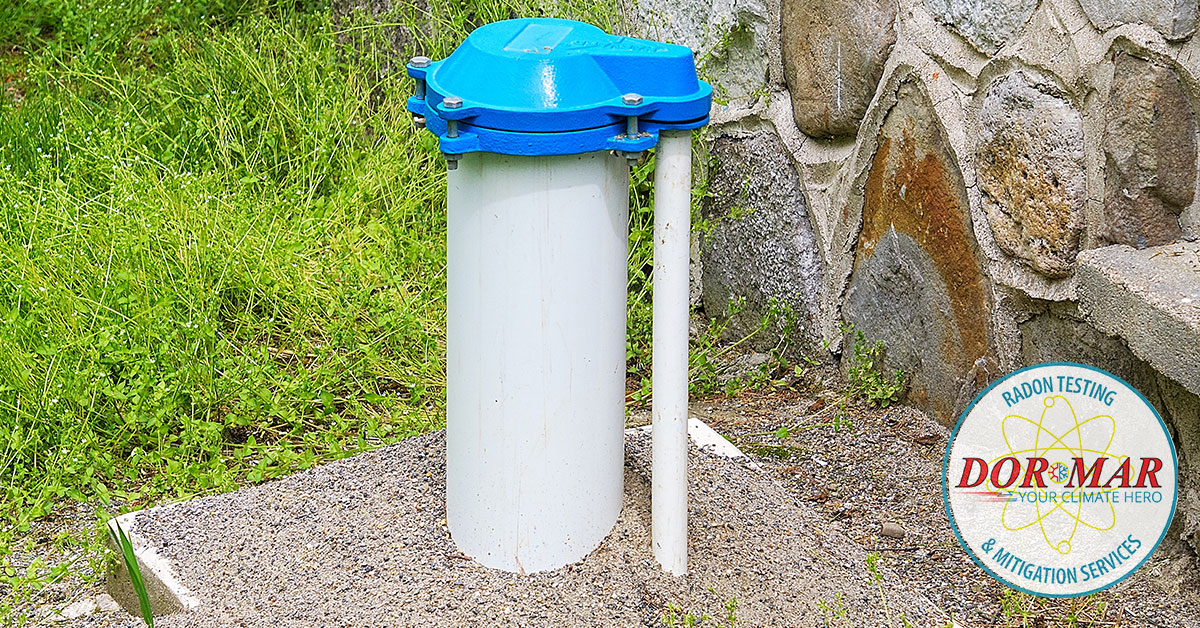
If radon is detected in your well water, installing a mitigation system is the best way to reduce risks.Aeration Systems: The Most Effective Solution
Aeration systems work by exposing water to air, allowing radon gas to escape before the water is used in the home. These systems are highly effective, removing up to 99% of radon. Common types of aeration systems include:- Spray aeration – Water is sprayed into an aeration chamber, where radon gas is vented outside.
- Bubble aeration – Air is injected into the water, forcing radon to rise and escape.
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Filtration
GAC filters use carbon to trap radon particles as water passes through. However, they have limitations:- They are less effective for high radon levels.
- They require frequent filter replacement to prevent buildup.
Final Thoughts on Radon in Well Water
Radon in well water is a serious but manageable risk. By testing regularly, using the right filtration systems, and taking preventative steps, homeowners can protect their families from this hidden danger.Don’t Wait – Get Your Home Tested for Radon
If you are not sure if your home has issues with radon gas, it’s best to get it tested. And it’s easy as a quick phone call Dor-Mar Radon Testing & Mitigation at (740) 675-1103 to arrange for a radon test. Or you can use the convenient form on our Radon Testing page.